Nifty Outlook Week Ending 3rd October 2025
In the week ending October 3, 2025, India’s benchmark indices — the Nifty 50 and the BSE Sensex — ended higher, notching up their second straight day of gains on Friday. This upward momentum followed a stretch of volatility and weakness earlier in the week.
On Friday, the Nifty 50 closed at 24,894.25, rising 57.95 points or 0.23%, while the BSE Sensex ended at 81,207.17, up 223.86 points or 0.28%.
Topics of Discussion
Nifty Outlook:Technical Analysis updated 6th October 2025
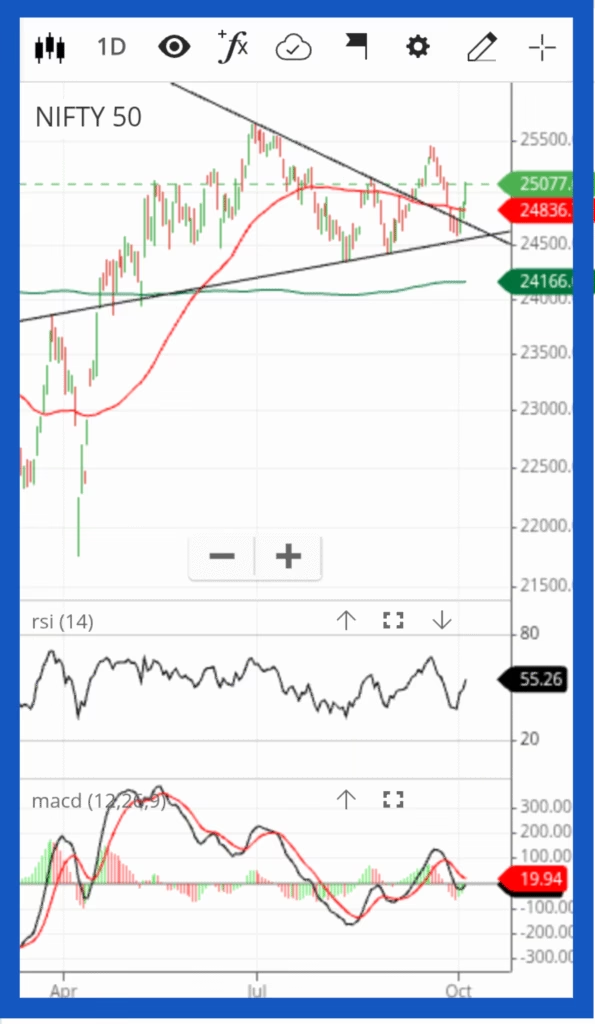
Source : Zerodha Kite: Last updated on 6th October 2025
🔍 Chart Overview
Pattern:
A long symmetrical triangle pattern that has been forming over several months.
Recent Price Action:
Nifty has broken out above the upper trendline of this triangle, signaling a potential bullish breakout.
Moving Averages:
The red line (50-day MA -24,836) is turning upward, showing short-term momentum improvement.
The green line (200-day MA) is still acting as a major long-term support near 24,166.
Indicators
RSI (14): Currently around 55, rising from lower levels — this suggests improving bullish momentum, but not yet overbought.
MACD: The MACD line is attempting to cross above the signal line from below — a bullish crossover may confirm in the coming sessions.
⚙️ Key Levels
Immediate Resistance: 25,077 – a close above this may confirm the breakout and open room toward 25,300–25,448
Support Zone: 24,836 (triangle retest zone) and 24,166 (200-DMA) — both crucial for maintaining bullish structure.
Interpretation by Smart Investello Research and Analysis
The long triangle breakage is a bullish sign, indicating that Nifty might have completed its consolidation phase.
If Nifty sustains above the breakout zone (around 24,800–25,000), it can lead to a fresh upward leg.
However, a fall back below 24,800 could make it a false breakout, so follow-up confirmation is essential.
Conclusion:
✅ Bullish bias above 24,800.
⚠️ Watch for sustained strength and volume above 25,000 for confirmation. Expected rally up to 25448~25500
Long-Term Nifty Outlook
Analysts remain optimistic.
Most analysts continue to maintain a positive long-term outlook for the Nifty 50 and the broader Indian equity market, citing strong domestic fundamentals. Robust economic indicators, rising domestic consumption, and a healthy earnings growth trajectory are expected to fuel a market rally from late 2025 into 2026.
Foreign investors see India as an attractive opportunity.
India has emerged as a favored investment destination for global investors, especially as capital flows shift away from China. Domestically, the growing influence of retail and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) is helping to counterbalance withdrawals by Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs), providing the market with greater stability. Historically, long-term investments in the Nifty 50 have yielded solid returns, reinforcing the case for a “buy-and-hold” strategy.
Key Growth Drivers
Government Policy:
Initiatives like GST 2.0 and sustained public sector spending are viewed as key drivers for growth, particularly in consumer-oriented and infrastructure sectors.
Financial Sector:
Continued credit expansion and attractive valuations make the banking and finance sector a compelling investment area.
Demographics:
India’s large and youthful population provides a long-term demographic advantage, supporting consumer growth and economic expansion.
Short-Term Nifty Outlook
Analysts expect consolidation.
In the near term, many analysts anticipate a phase of consolidation and continued volatility for the Nifty 50. The index is expected to remain range-bound unless it clearly breaks out of its current levels. For example, Sumeet Bagadia of Choice Broking sees a short-term trading range of 24,500–24,900, suggesting a significant move outside this range would indicate the next directional trend.
Investor Sentiment and Activity
FIIs are cautious.
Throughout most of 2025, FIIs have been net sellers of Indian equities, withdrawing over ₹2 lakh crore year-to-date. This pullback is attributed to high valuations, trade tensions with the U.S., and a shift in focus toward better-performing global markets.
DIIs and retail investors remain resilient.
Despite the FII exits, DIIs and retail investors have absorbed much of the selling pressure, continuing to invest through mechanisms like Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs). This ongoing domestic support has helped stabilize the market.
Potential Headwinds
High Valuations:
Some market segments, especially mid-cap and small-cap stocks, are considered overvalued, raising the risk of a market correction.
Earnings Slowdown:
Earnings growth for Nifty 50 companies has recently lost momentum, and a sharper rebound may be necessary to sustain current valuations.
Global Uncertainty:
Global factors such as U.S. interest rate decisions and macroeconomic conditions continue to impact investor sentiment and FII behavior.
Key Insights
In summary, while short-term caution persists due to high valuations and mixed signals from foreign investors, the long-term outlook remains broadly positive. India’s strong economic fundamentals, supportive government policies, and resilient domestic investor base offer a solid foundation for future market growth. Many FIIs appear to be in a “wait-and-watch” mode, with expectations that renewed earnings growth and easing global uncertainty could prompt them to re-enter the market with higher allocations.
Factors Influencing the Nifty 50: Domestic and Global
Domestic Factors
Economic Indicators:
Strong GDP growth, low inflation, and low unemployment typically boost investor confidence and corporate earnings, positively affecting the Nifty 50. India’s Q1 GDP growth of 7.8% was a notable positive, although concerns persist about a potential slowdown in urban consumption and earnings growth.
Inflation & Interest Rates:
High inflation erodes consumer purchasing power and increases business costs, potentially squeezing corporate profits. Historically, inflation between 3–5% has correlated with strong index returns in India, while rates above 6–7% tend to dampen performance.
Monetary Policy:
Decisions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)—particularly regarding interest rates like the repo rate—directly affect liquidity, borrowing costs, and stock valuations.
Corporate Earnings:
Strong earnings growth generally leads to rising stock prices, while weak earnings can depress investor sentiment.
Government Reforms:
Policy decisions around taxation, regulations, and spending—particularly on infrastructure—can stimulate economic activity or create uncertainty. For instance, changes in capital gains and income tax policies can influence both investment behavior and consumer spending.
FII & DII Flows: Large FII inflows typically boost stock prices, while heavy outflows may create downward pressure. However, rising DII and retail investor participation is helping buffer these impacts.
Sector Performance:
Nifty’s performance is also shaped by trends within major sectors like banking, IT, and energy. For example, the banking sector is highly sensitive to interest rate movements.
Investor Sentiment:
Market sentiment, shaped by news, economic outlook, and emotional responses, can drive sharp moves either way.
Also Read
Why KEI Industries Could Be a Strong Buy for 2025 and Beyond
Global Factors
Global Economic Trends:
International market trends—such as movements in the S&P 500 or Dow Jones—along with economic data and geopolitical developments, can have a strong influence on the Nifty 50. For example, fears of a potential U.S. recession can dampen sentiment globally.
Geopolitical Events:
Conflicts (such as the Israel-Hamas conflict mentioned in August 2024), trade tensions, and financial crises introduce uncertainty and market volatility.
FII Activity:
Global risk sentiment and monetary conditions influence whether FIIs invest in Indian markets. Weak international markets or rising interest rates in developed economies often lead to capital outflows from India.
Commodity Prices:
Volatility in global commodity prices—especially crude oil, a major import—can affect inflation, the trade balance, and corporate profits. Rising oil prices often hurt the rupee and, in the short term, the Nifty 50, although this relationship is less consistent over longer periods due to India’s dominant service economy.
Exchange Rates:
A weakening rupee raises import costs, reducing profitability for import-heavy businesses.
Conclusion :
As of October 3, 2025, the Nifty 50 remains in a phase of cautious consolidation, reflecting global uncertainties and persistent FII outflows. However, India’s resilient domestic investors, solid economic fundamentals, and policy-driven growth outlook continue to underpin long-term optimism. While short-term volatility may persist, especially amid elevated valuations and uneven earnings growth, the broader market narrative remains constructive. With government reforms, demographic strength, and improving consumption trends, India stands well-positioned for a renewed rally in 2026. Prudent investors may view the current consolidation phase as an opportunity to accumulate quality stocks with a long-term horizon.
Further Reading
SIP and Lumpsum : Using Data to Find the Perfect Mix in 2025
SIP and Lumpsum - Use data-backed insights to find the ideal investment mix in 2025. Maximize returns with a balanced, research-driven mutual fund strategy.
Read More →Parag Parikh FlexiCap Fund | Should You Buy at ₹113 Cr AUM? | Fund Review 2025
Parag Parikh FlexiCap Fund’s AUM crossed ₹113 Cr. Is it still the right time to invest? Get expert insights, risk analysis, and data-backed report here.
Read More →


